← Back to Projects

SemTTI
Mentored by: Applied Materials
Framework for generating realistic SEM images from segmentation masks, sketches, or text

Python
PyTorch
Pix2Pix
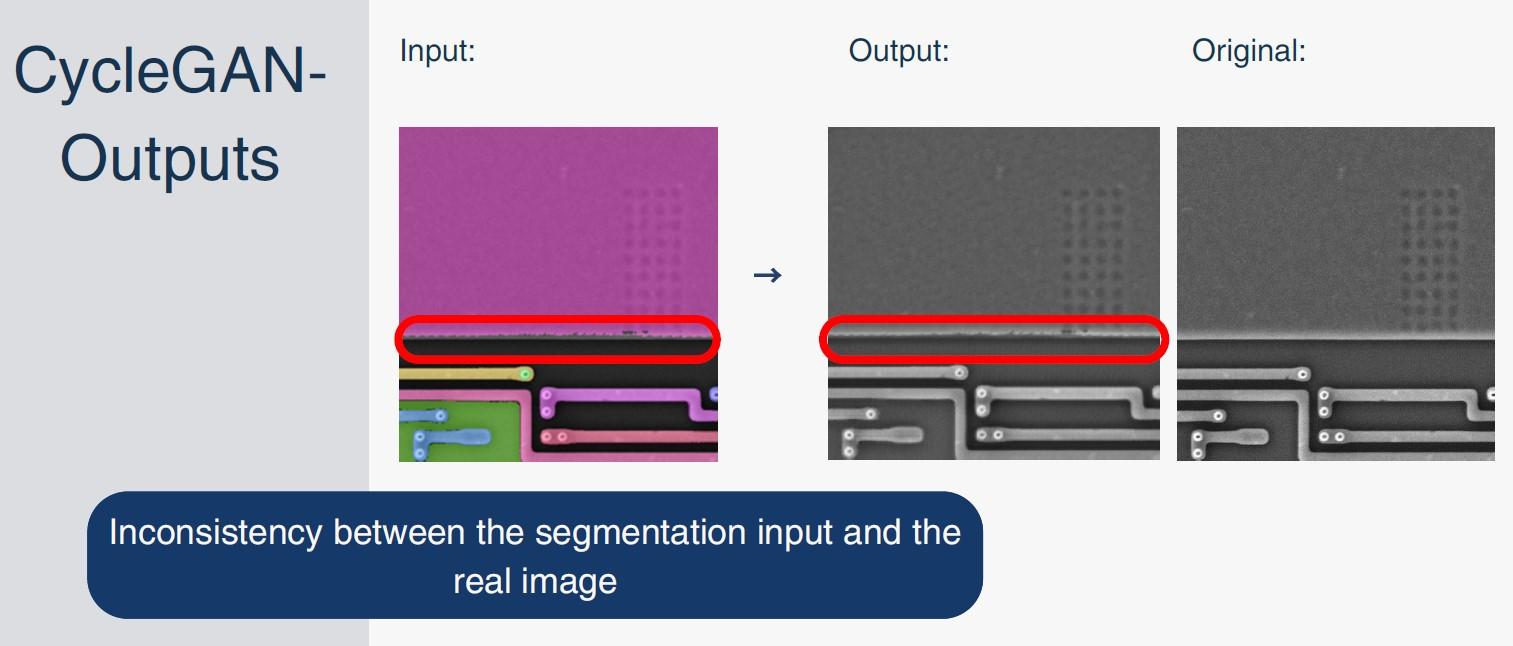
CycleGAN
Stable Diffusion Textual Inversion
OpenCV
SAM-2
Docker
Description
Three generative pipelines: (1) Segmentation→SEM using Pix2Pix and CycleGAN; (2) Sketch→SEM via Pix2Pix; (3) Text→SEM exploration using tagging models and textual inversion. Includes dataset building with Meta SAM-2, GAN training (CycleGAN up to 300 epochs, Pix2Pix 150 epochs), FID/KID/LPIPS/PSNR/SSIM evaluation, classifier-based realism testing, and failure-case analysis (artifacts, domain mismatch).
Mentors
Team Members
Cohort: Data Science Bootcamp 2025 (Data)
Responsibilities:
Research: Segmentation data augmentation for training – Implemented two masking approaches: training a U-Net model from scratch and applying OpenCV contour methods to identify layered regions.
Experimented with Stable Diffusion’s Textual Inversion by training custom embeddings in PyTorch on Kaggle GPUs to capture SEM-specific textures and patterns, evaluating their effect on improving realism in generated SEM images.
Trained a Pix2Pix model in PyTorch on Kaggle GPUs to convert Canny-based sketch inputs into realistic SEM images, including dataset construction, image preprocessing with OpenCV/NumPy, and model evaluation using FID, KID, SSIM and additional metrics.
Research: Add SEM noise to synthetic images – Added SEM-style noise by blending sampled noise patches from real SEM images and testing Gaussian/Poisson noise, with exploration of a future trained noise-injection model.
E
No preview image
Responsibilities:
CLIP Input Analysis and Pipeline Mapping: Investigated CLIP’s input structure and internal pipeline to determine how textual and visual embeddings are processed and whether the generator must run externally or as part of CLIP’s native flow.
CLIP Variant Evaluation and Deployment: Compared multiple CLIP variants (e.g., ViT-based architectures), selected the optimal version, deployed it on the remote GPU server, and validated its performance for downstream tasks.
Comparative Model Analysis (SDXL vs. SD 0.1) Authored a detailed comparative analysis of two generative architectures—including training objectives, noise schedulers, latent resolutions, and semantic alignment—and evaluated their suitability for SEM simulation.
Textual Inversion Evaluation on SDXL: Trained and tested Textual Inversion embeddings on SDXL for SEM-specific conditioning, and evaluated model behavior to detect embedding instability, noise inconsistencies, and edge-artifact degradation.
Classification Gap Investigation: Analyzed why the classification model achieves near-perfect separation between real and generated SEM images, and authored a technical summary detailing root causes and mitigation strategies.
Noise & Edge-Artifact Evaluation in Segmentation-Based Generation: Studied the impact of missing noise patterns and edge-artifacts in images generated from segmentation masks, experimented with techniques to simulate realistic SEM noise, and evaluated edge-reduction methods to minimize detectable discrepancies between real and mask-generated outputs.
...and more contributions not listed here
Responsibilities:
Research: Explored and compared LLMs such as LLaMA and Gemma, focusing on their capabilities and key differences.
Developed a full GUI application that receives text input from the user, sends it to an LLM, returns the model’s output to the client - and containerized the entire system with Docker.
Research: Explored image-to-text models such as PromptCap and Florence, comparing their outputs and understanding how they generate labels from images.
Research: Trained Textual Inversion on the Stable Diffusion SDXL model to enable it to learn and generate the desired image style.
Trained a CycleGAN model on SEM and SEG images to enable translation between the two domains.
Performed metric evaluation on the results (as FID, PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, and more), and compared the performance with other models trained on the same images.
Trained a classification model on real and generated images to evaluate how well it distinguishes between them, expecting a score around 0.5, but the results were poor - approximately 0.9.
If more time were available, the next steps would include adding additional training, exploring explainability methods to understand how the model makes its distinctions, and training a model using the generated images to test how well it later performs on real images. If the model performs well on real data after being trained on synthetic data, it would indicate that the core goal of the project was successfully achieved.
...and more contributions not listed here
Responsibilities:
Research - on Textual Inversion: Explored Textual Inversion techniques, including embedding creation and integration into SDXL, to evaluate potential improvements in generation quality.
Research - Feature Extraction for Dataset Labeling: Used OpenCV to extract morphological and structural features from SEM images for dataset labeling and analysis, including attempts to extract descriptive text from features.
Dataset Creation using Meta’s SAM-2: Used Meta’s SAM-2 segmentation model to create accurate structural masks for real SEM images and build a paired dataset (mask → image) needed for training and evaluating generative models.
Pix2Pix Training (Segmentation → Image): Prepared datasets, configured experiments, and trained a Pix2Pix model to generate SEM images from segmentation maps, including epoch tracking, result analysis, and parameter tuning.
Model Evaluation Metrics Development: Designed evaluation metrics and analysis tools to compare real and generated images, assessing structural accuracy, texture fidelity, and overall realism.
Investigating Differences Between Real and Generated Images: Analyzed noise patterns, frequency characteristics, and imaging artifacts to understand the root causes of discrepancies between generated and real SEM images.
Research - Noise Modeling & Enhancement: Added a learnable noise layer to the model, designed to capture SEM-specific noise patterns during training and re-inject them during generation, in order to test whether data-driven noise could improve realism and enhance model performance.
Documentation & Results Presentation: Produced research summaries, visual comparisons, and presented findings and insights to mentors and the project team.
...and more contributions not listed here


